Fix ‘This PC Can’t Run Windows 11’ Error and How to Bypass

Ever since Windows 11’s release, we’ve all been itching to get our hands on its new features and slick design. But during installation, you hit a snag – the dreaded “This PC can’t run Windows 11” error. This message pops up because your computer’s hardware doesn’t quite tick all the boxes for the new OS. While Microsoft has these requirements in place for security reasons, it can be a bummer if your current machine feels perfectly capable.
This guide will equip you to tackle this error. We’ll explore alternative solutions that ensure your system runs smoothly and securely with Windows 11. However, if upgrading hardware isn’t on the table, we’ll cautiously walk you through methods to bypass Windows 11 requirements. But be warned, there are inherent risks involved in bypassing these checks. We’ll provide a general overview of the process while emphasizing the importance of caution and thorough research before making any major system changes.
Learn About “Why Can’t My PC Run Windows 11” and Its Reasons
The “This PC can’t run Windows 11” error message is a roadblock you might encounter when trying to install Windows 11 on your device. It essentially means your PC doesn’t meet the minimum requirements set by Microsoft for running Windows 11 OS.
There are a few key reasons why this error occurs. They’re discussed below:
Security Features
Windows 11 prioritizes security, and some hardware features are now mandatory. Two important ones are:
- Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0: This chip enhances security by storing encryption keys and helps protect against malware attacks.
- Secure Boot: This firmware feature ensures only authorized software loads at startup, preventing malicious programs from taking hold. If your computer lacks TPM 2.0 or Secure Boot is disabled, you’ll likely see this error.
Processor Compatibility
Microsoft requires processors from a specific generation (generally newer Intel 8th Gen or AMD Ryzen 2000 and later) to ensure optimal performance and security features for Windows 11.
Other Hardware Requirements
While less common, not having enough RAM (memory or storage space) can also trigger the error message.
What to Do If My PC Can’t Run Windows 11?
If the PC can’t run Windows 11, it throws ‘This PC can’t run Windows 11’ message towards you. This might throw a wrench in your upgrade plans. But fear not! There are solutions. A few of them in fact! We’ll explore a few approaches addressing the compatibility issues for a secure and recommended upgrade, and how you can bypass the error message. But just remember that, you need to proceed with caution as system security is paramount. Let’s delve into the options to get you on your way to Windows 11.
Try Enabling TPM 2.0 in BIOS
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0 is a security chip that’s often a requirement for running Windows 11. If you encountered this error message, and suspect that TPM 2.0 might be disabled, you can try enabling it in your BIOS. We’ll mention a general guide to enable it, but remember the specific steps will vary depending on your motherboard manufacturer.
- Check your Motherboard Manual: This is the best resource for finding specific instructions on enabling TPM 2.0 in your BIOS. To check your TPM version, follow these steps:
- Launch ‘Run’ by pressing the Windows button +R simultaneously.
- A short window with the title ‘Run’ will pop up. Type ‘tpm.msc’ in the text box and press enter.
3. A window with the title “Trusted Platform Module (TPM) Management on Local Computer” will open up.
4. From that window, check the “Status” Section. You’ll see the message “The TPM is ready for use.” And to check the version, take a look at the “TPM Manufacturer Information” and if the “Specification Version” says “2.0”, you’re ready to go!
5. But just ensuring it doesn’t mean your TPM is activated. If your TPM is disabled, you’ll See the message “Compatible TPM cannot be found”.
- Enable TPM: To enable TPM, you need to open your BIOS settings and follow the steps mentioned below:
- Restart your computer and Enter BIOS.
2. Navigate to the Security or Advance Tab. This tab’s name might vary depending on your BIOS. One is shown below:
3. In the ‘Advanced’ tab, look for ‘PCH-FW Configuration’ or ‘Trusted Computing’ or ‘TPM Embedded Security’ option.
4. Look for TPM Related Options. You might see options like ‘TPM’, ‘Intel Platform Trust Technology (IPTT)’, or ‘AMD CPU fTPM’. Enable it, and then Save and Exit from the BIOS menu.
For further support, you can visit Microsoft’s Page here!
Try Enabling Secure Boot in BIOS
Secure Boot is a security feature in your BIOS that verifies the legitimacy of software before it loads during startup. It helps prevent malicious programs from taking hold of your system. If you encountered the “This PC can’t run Windows 11” error and suspect Secure Boot might be disabled, you can try enabling it in your BIOS. Here’s a general guide, but remember the specific steps will vary depending on your motherboard manufacturer.
- Check Your Motherboard Secure Boot Status: This is the best resource for finding specific instructions on enabling Secure Boot in your BIOS. To check if your PC has it enabled or not, follow the instructions below:
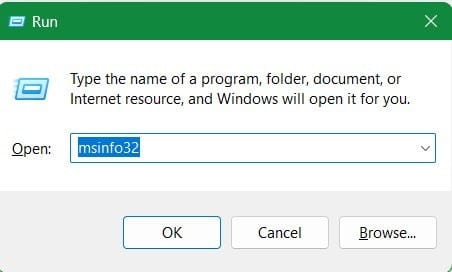
- Launch ‘Run’ by pressing the Windows button +R simultaneously.
- A short window with the title ‘Run’ will pop up. Type ‘msinfo32’ in the text box and press enter.
3. A window with the title “System Information” will pop up. There, under ‘System Summary’, search for ‘Secure Boot State’. If it’s ‘On’, then you have nothing to worry about.
4. But if your Secure Boot State is not enabled, you’ll see the window like this:
- Enable Secure Boot in BIOS: To enable Secure Boot State, you need to open your BIOS settings and follow the steps mentioned below:
- Restart your computer and Enter BIOS.
- Navigate to the Security or Advance Tab. This tab’s name might vary depending on your BIOS. One is shown below:
3. Go to the ‘Security’ category, and search for the option ‘Secure Boot’.
4. You’ll see options under that section, look for the ‘Secure Boot Control’. Enable that option, if disabled.
5. Save Changes and Exit BIOS. This usually involves pressing a key like F10 and confirming that you want to save the changes.
If you want to know more, check out Microsoft guide on checking Secure Boot status here!
Checking Processor Compatibility for Windows 11
While enabling TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot can address some compatibility issues for Windows 11, your processor also plays a crucial role. Here’s how to ensure your processor meets the minimum requirements for running Windows 11:
- Using PC Health Check App: Microsoft offered a PC Health Check app to check system compatibility for Windows 11. While it’s no longer available for download, you might find it pre-installed on some systems. If you have it, launch the app and run a scan to see if your processor is compatible.
- Microsoft Documentation: Microsoft provides a list of supported processors for Windows 11 on their website. You can search for “Windows 11 supported processors” to find the specific document. This list categorizes processors by manufacturer (Intel, AMD, etc.) and generation. Look for your processor model and generation in the list to confirm compatibility.
- Checking Processor Information:
- From Settings: Open the Windows Settings app. Go to “System” and then “About.” Under “Device specifications,” look for the “Processor” entry. This will display your processor model and generation.
2. From Task Manager: Open the Windows Menu and search for ‘Task manager’. From that, go to the ‘Performance’ submenu and click on ‘CPU’, there on the top right, your Processor information will be visible.
If your CPU is not up to the mark, we recommend you upgrading your motherboard and CPU to a model that meets Windows 11 requirements is the most secure and future-proof solution.
How to Bypass ‘This PC Can’t Run Windows 11’
However, if you can’t follow any of the steps mentioned above, you can always bypass the system compatibility check to install Windows 11 in your PC. We’ll mention about how you can workaround the system requirements check below:
Before we begin, a word of caution though! Older PCs might not function properly with Windows 11. This includes certain features not functioning properly, and there’s a possibility that your Windows version might get corrupted or start malfunctioning. For this reason, Microsoft doesn’t recommend installing Windows 11 in a device that’s unsupported in Microsoft’s eyes. Moreover, we can’t guarantee if you’ll get all the future updates. So, it’s always better to practice caution in whatever you do!
Now that’s out of the way, let’s take a look at how you can bypass the system requirement check using the Windows Registry.
Windows Registry is a sensitive directory for your PC. Any mess up there, and you’ll lose access to use your PC! So, if you’re still proceeding, it’s better to make a backup for your Registry so that you can restore it before the damage is done. About this, you can use a registry cleaner. It’ll back up your Registry Data automatically and restore the Registry for you.
So, here’s a breakdown on how you can complete the process:
- Launch ‘Run’ by pressing the Windows button +R simultaneously.
- A short window with the title ‘Run’ will pop up. Type ‘regedit’ in the text box and press enter.
3. Once the Registry Editor Opens Up, from the left drop down menus, find “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE’. A series of submenus will drop down and then find ‘SYSTEM’. Then select ‘MoSetup’ from the ‘Setup’ menu. You’ll see a window like this:
4. However, if you can’t find the ‘MoSetup’ folder, you need to create one yourself by right clicking on the ‘Setup’ section and Select ‘Key’ from the ‘New’ option. And finally rename that newly created key with ‘MoSetup’.
5. When you get inside the MoSetup directory, right click on any empty section of the window and select ‘DWORD (32-bit) Value’ under the ‘New’ option. A new entry will be created. Rename the new entry as “AllowUpgradesWithUnsupportedTPMorCPU”.
Double-click on the entry you just created and set its value as 1 under the ‘Value data’ section. And then Press OK.
6. Thus, you’ll be able to bypass the TPM 2.0 and CPU limitations while installing Windows 11.
7. For other requirements, such as Secure Boot, Ram, and others, you can bypass by creating another directory in the ‘Setup’ section from Step 3. So, to proceed, create another directory (follow Step 4 if you’re confused) named ‘LabConfig’ in the ‘Setup’ directory as we already mentioned.
8. After you’re inside the ‘LabConfig’, create ‘DWORD (32-bit) Value’ files (similar step as Step 5) naming them: ‘BypassTPMCheck’ for Bypassing TPM, ‘BypassCPUCheck’, ‘BypassRAMCheck‘, ‘BypassSecureBootCheck’, and ‘BypassStorageCheck’.
After creating them, double click on the files and change their value data to 1 (Similar to Step 5).
After you’re done creating these, download the Official Windows 11 OS from the Microsoft Site. after that, we can provide you an activation key once you purchase the Windows 11 Pro License key from Msckey, and casually install the Windows as you usually do. We sure hope after this step, there wouldn’t be any issue installing the OS in your device!
Final Words
The decision to upgrade to Windows 11 is yours. This guide explored various solutions to the “This PC can’t run Windows 11” error message. We emphasized the importance of addressing compatibility issues for a secure and smooth experience. Upgrading your hardware or sticking with Windows 10 are often the safest choices.
If you decide to bypass error messages through registry editing, remember: proceed with extreme caution. The risks to your system’s security and stability are significant. Make sure you understand the potential consequences and prioritize the health of your system.
Hopefully, this guide has equipped you to make an informed decision about upgrading to Windows 11. Whether you choose to embrace the new OS, optimize your current system, or wait for future developments, prioritize security and system stability for a positive computing experience. Get your PC ready for the latest Windows 11 upgrade – follow our simple steps now!